In the complex landscape of pain management, finding effective relief is often challenging. Chronic pain, resulting from conditions such as arthritis, surgery, or injury, can significantly impact one’s quality of life.
Among various medications, Percocet Pills is a potent option. This combination of oxycodone, an opioid, and acetaminophen, a non-opioid pain reliever, offers substantial pain relief. However, it also presents risks, including the potential for abuse. This article explores the role of Percocet Abuse in pain management, focusing on balancing relief with safety and addressing the risk of misuse.
Understanding Percocet Pills
Percocet combines oxycodone and acetaminophen. Oxycodone is a powerful opioid analgesic that alleviates moderate to severe pain by altering the brain’s perception of pain. Acetaminophen enhances the pain-relieving effects of oxycodone and can reduce fever. This combination makes Percocet an effective medication for pain management, often prescribed after surgeries, injuries, or for conditions causing significant discomfort.
The Role of Percocet in Pain Management
For individuals experiencing acute pain, Percocet Pill can provide significant relief. Its rapid onset allows patients to manage pain effectively and return to their daily activities, improving overall quality of life. In post-surgical scenarios, effective pain management with Percocet can support quicker recovery and rehabilitation.
Additionally, this medication is valuable for managing chronic pain conditions that do not respond well to over-the-counter options. It can help alleviate pain from severe arthritis, cancer, or nerve damage, enabling patients to participate in physical therapy and other necessary activities.
Risks and Side Effects
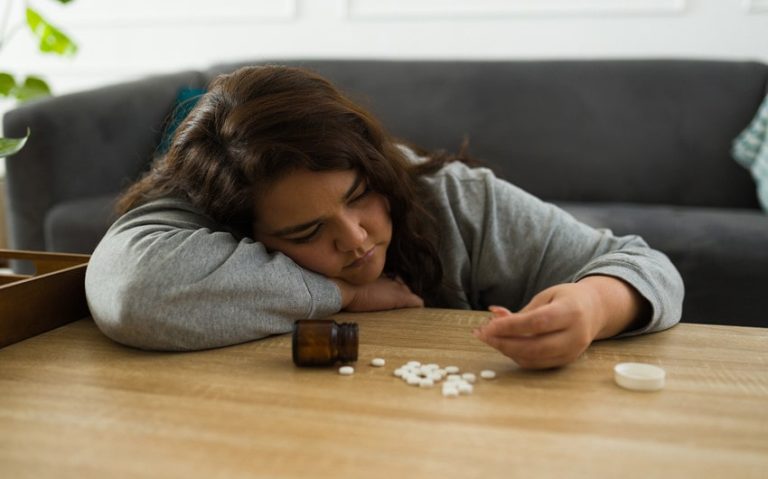
Despite its effectiveness, Percocet abuse has notable risks, mainly due to its opioid component. Opioids can lead to misuse, dependence, and addiction. The risk of abuse increases with prolonged use and higher doses, as patients may develop tolerance and require more of the medication to achieve the same relief, leading to potential misuse.
Common side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, constipation, and nausea. More severe side effects, such as respiratory depression, can occur if the medication is not used as prescribed. Respiratory depression, where breathing becomes inadequate, can be life-threatening.
Acetaminophen, while generally safe at recommended doses, poses risks of its own. Excessive intake can result in liver damage, a serious and potentially fatal condition. Adhering to the prescribed dosage and avoiding other acetaminophen-containing products is crucial.
Addressing Percocet Abuse
Abuse of Percocet is a serious concern that can lead to addiction, overdose, and other health issues. Misuse of this medication—whether by taking it in higher doses than prescribed, using it without a prescription, or consuming it in unintended ways (such as crushing and snorting)—increases the risk of addiction.
Recognizing the Signs of Abuse
- Increased Tolerance: Needing more of the medication to achieve the same relief.
- Compulsive Use: Taking Percocet more frequently or in higher doses than prescribed.
- Neglect of Responsibilities: Failing to meet work, school, or family obligations due to medication use.
- Physical Symptoms: Experiencing symptoms like euphoria, drowsiness, or mood swings.
Preventing Abuse
- Strict Adherence to Prescriptions: Follow the prescribed dosage and schedule precisely.
- Secure Storage: Store Percocet Abuse in a secure location to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Monitoring: Healthcare providers should monitor usage and look for signs of misuse or addiction.
- Patient Education: Educate patients about the risks of abuse and the importance of responsible use.
Safe Use of Percocet
To balance relief and safety with Percocet, consider the following strategies:
1. Strict Adherence to Prescriptions: Patients should take Percocet exactly as prescribed, including dosage and timing. Any changes should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
2. Regular Monitoring: Healthcare providers should regularly assess the effectiveness of the medication and adjust the dosage as necessary. Monitoring can help identify early signs of misuse or addiction.
3. Short-Term Use: Whenever possible, prescribe Percocet Pill for the shortest duration needed to manage acute pain. For chronic pain, explore other treatment options and use Percocet as part of a comprehensive pain management plan.
4. Patient Education: Educate patients about the risks associated with Percocet Abuse and the potential for misuse. Ensure they understand the signs of addiction and the importance of not sharing their medication.
5. Use of Adjunctive Therapies: Incorporate non-pharmacological therapies such as physical therapy, acupuncture, and cognitive-behavioral therapy to manage pain more holistically and reduce reliance on Percocet Pill.
Alternatives to Percocet
Given the risks of opioids, exploring alternative pain management options is essential. Non-opioid pain relievers like NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can be effective for many types of pain. For neuropathic pain, medications such as gabapentin or pregabalin might be prescribed.
Interventional procedures like nerve blocks, epidural injections, or spinal cord stimulation can also provide significant relief for specific pain conditions. These methods can target the source of pain more directly, potentially reducing the need for systemic medications.
The Role of Multidisciplinary Pain Management
Effective pain management often requires a multidisciplinary approach. A team of healthcare providers—including pain specialists, physical therapists, psychologists, and occupational therapists—can develop a comprehensive pain management plan. This approach addresses the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of pain, leading to better patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Percocet Pill can be a valuable tool in pain management, offering significant relief for those suffering from moderate to severe pain. However, its use must be carefully managed to balance the benefits with the risks of dependence, abuse, and other adverse effects.
Through strict adherence to prescriptions, regular monitoring, patient education, and the incorporation of alternative therapies, healthcare providers can help patients navigate the complexities of pain management safely and effectively. By doing so, they ensure that patients achieve the relief they need while minimizing potential harms associated with Percocet.